From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Nawabzada Liaquat Ali Khan (Næʍābzādāh Liāqat Alī Khān  listen (help·info),Urdu: لیاقت علی خان; born October 1895 – 16 October 1951), widely known as Shaheed-e-Millat[1] (Urdu: شہید ملت Martyr of the Nation), was one of the leading Founding Fathers[2] of modern Pakistan, statesman, lawyer, and political theorist who became and served as the first Prime Minister of Pakistan; in addition, he was also the first Defence Minister of Pakistan, the first Finance Minister of India, and the minister of Commonwealth and Kashmir Affairs from 1947 until his assassination in 1951.[2][2] It has been alleged that the Afghan and US governments were involved in his assassination, although this claim has not merited any substantial evidence.[3]
listen (help·info),Urdu: لیاقت علی خان; born October 1895 – 16 October 1951), widely known as Shaheed-e-Millat[1] (Urdu: شہید ملت Martyr of the Nation), was one of the leading Founding Fathers[2] of modern Pakistan, statesman, lawyer, and political theorist who became and served as the first Prime Minister of Pakistan; in addition, he was also the first Defence Minister of Pakistan, the first Finance Minister of India, and the minister of Commonwealth and Kashmir Affairs from 1947 until his assassination in 1951.[2][2] It has been alleged that the Afghan and US governments were involved in his assassination, although this claim has not merited any substantial evidence.[3]
Born in house of mandal Nousherwan and hailed from Karnal, East Punjab, Ali Khan was educated at the Aligarh Muslim University in India, and then theOxford University in the United Kingdom.[4] Well educated, he was an Islamic democracy political theorist who promoted the parliamentarism in India. After being invited by the Congress Party, he opted for the Muslim League led by influential Mohammad Ali Jinnah who was advocating and determining to eradicate the injustices and ill treatment meted out to the Indian Muslims by the British government.[4][5] He pushed his role in the independence movements of India and Pakistan, while serving as the first Finance Minister in the interim government of British Indian Empire, prior to the independence ofPakistan in 1947.[5] Ali Khan assisted Jinnah in campaigning for the creation of a separate state for Indian Muslims.[6]
Ali Khan's credentials secured him the appointment of Pakistan's first Prime Minister, Ali Khan's foreign policy sided with the United States and the West, though his foreign policy was determined to be a part of the Non-Aligned Movement.[7] Facing internal political unrest, his government survived a couphatched by the leftists and communists. Nonetheless, his influence grew further after Jinnah's death, and he was responsible for promulgating theObjectives Resolution. In 1951, at a political rally in Rawalpindi, Ali Khan was assassinated by a hired assassin, Sa'ad Babrak.[4][7]
He is Pakistan's longest serving Prime Minister spending 1,524 days in power, a record which has stood for 63 years to the present
Family background[edit]
Liaquat Ali Khan was born into a Muslim — (lit. Noble) Jatt Mandal Nousherwani family in Karnal,[9] Eastern Punjab of India, on 1 October 1895.[10] His father, Nawab Rustam Ali Khan, possessed the titles of Rukun-al-Daulah, Shamsher Jang andNawab Bahadur, by the local population and the British Government who had wide respect for his family. The Ali Khan family was one of the few landlords whose property (300 villages in total including the jagir of 60 villages in Karnal) expanded across both eastern Punjab and the United Provinces.[11] The family owned pre-eminence to timely support given by Liaqat's grandfather Nawab Ahmed Ali Khan of Karnal to British army during 1857 rebellion.(source-Lepel Griffin's Punjab Chiefs Volume One). Liaquat Ali Khan's mother, Mahmoodah Begum, arranged for his lessons in the Qur'an andAhadith at home before his formal schooling started.[12] His family had strong ties with the British Government, and the senior British government officers were usually visited at his big and wide mansion at their time of visit.[12]
His family had deep respect for the Indian Muslim thinker and philosopher Syed Ahmad Khan, and his father had strong views and desires for young Liaqat Ali Khan to educated in the British educational system; therefore, his family admitted Ali Khan to famous Aligarh Muslim University (AMU) to study law and political science. Ali Khan was sent to Aligarh to attend the AMU where he would obtained degrees in law and political science.
In 1913, Ali Khan attended the Muhammadan Anglo Oriental College (now Aligarh Muslim University), graduating with aBSc in Political science and LLB in 1918, and married his cousin, Jehangira Begum, also in 1918.[13] After the death of his father in 1919, Ali Khan, with British Government awarding the grants and scholarship, went to England, attending theOxford University's Exeter College to pursue his higher education.[12] In 1921, Ali Khan was awarded the Master of Law in Law and Justice, by the college faculty who also conferred him with a Bronze Medallion.[12] While a graduate student at Oxford, Ali Khan took active participation in student unions and was an elected Honorary Treasurer of the Majlis Society— a student union founded by Indian Muslim students to promote the Indian students rights at the university.[12] Thereafter, Ali Khan was called to joined the Inner Temple, one of the Inns of Court in London.[12] He was called to the Bar in 1922 by one of his English law professor, and starting his practices in law as an advocate.[11]
Political activism in British India[edit]
Ali Khan returned to his homeland Britain in 1923, entering in national politics, determining to eradicate to what he saw as the injustice and ill-treatment of Indian Muslims under the British Indian Government and the British Government.[12] His political philosophy strongly emphasis a united India, first gradually believing in the Indian nationalism. The Congress leadership approached to Ali Khan to become a part of the party, but after attending the meeting with Jawaharlal Nehru, Ali Khan's political views and ambitions gradually changed.[12] Therefore, Ali Khan refused, informing the Congress Party about his decision, and instead joining the Muslim League in 1923, led under another lawyer Muhammad Ali Jinnah. Soon Jinnah called for an annual session meeting in May 1924, in Lahore, where the goals, boundaries, party programmes, vision, and revival of the League, was an initial party agenda and, was carefully discussed at the Lahore caucus. At this meeting, Khan was among those who attended this conference, and recommending the news goals for the party.[12]
United Province legislation[edit]
Ali Khan initially compaigned in the 1926 elections from the rural Muslim constituency of Muzzaffarnagar for the provisional legislative council.[14] Ali Khan won the elections with unanimously and with heavy margin, whilst there were no opponents that campaign against him.[14] After taking the oath, Ali Khan embarked his parliamentary career, representing the United Provinces at the Legislative Council in 1926.[14] In 1932, he was unanimously elected Deputy President of UP Legislative Council.[11][14]
During this time, Ali Khan intensified his support in Muslim dominated populations, often raising the problems and challenges faced by the Muslim communities in the United Province.[14] Ali Khan joined hands with academician Sir Ziauddin Ahmed, taking to organize the Muslim students communities into one student union, advocating for the provisional rights of the Muslim state.[14] His strong advocacy for Muslims rights had brought him into national prominence and significant respect was also gained from Hindu communities whom he also fought for them at higher hierarchy of the government.[14]Ali Khan remained the elected member of the UP Legislative Council until 1940, when he was proceeded to elect to theCentral Legislative Assembly; he participated actively, and was the influential member in legislative affairs, where his recommendations would also noted by other members.[14]
In his parliamentary career, Ali Khan established his reputation as "eloquent principled and honest spokesman" who would never compromised on his principles even in the face of severe odds.[15] Ali Khan, on several occasions, used his influence and good offices for the liquidation of communal tension and bitterness.[15]
Allying with Muslim League[edit]
Ali Khan rose to became one of the influential members of the Muslim League, and was one of the central figure in the Muslim League delegation that attended the National Convention held at Calcutta.[16] Earlier the British Government had formed the Simon Commission to recommend the constitutional and territorial reforms to the British Government.[16] The commission, compromising the seven British Members of Parliament, headed under its Chairman Sir John Simon, met briefly with Congress Party and Muslim League leaders.[16] The commission had introduced the system of dyarchy to govern the provinces of British India, but these revision met with harsh critic and clamoured by the Indian public.[16] Motilal Nehru presented his Nehru Report to counter British charges.[16] In 1928, Ali Khan and Jinnah decided to discuss the Nehru Report in December 1928.[17] In 1930, Ali Khan and Jinnah attended the First Round Table Conference, but it ended in disaster, leading Jinnah to depart from British India to Great Britain.[17] During this meantime, Ali Khan's second marriage took place in December 1932. His wife, Begum Ra'ana, was a prominent economist and an educator.[18] She, too, was an influential figure in the Pakistan movement.[18]
Ali Khan firmed believed in the unity of Hindu-Muslim community, and worked tirelessly for that cause.[16] In his party presidential address delivered at the Provisional Muslim Education Conference at AMU in 1932, Ali Khan expressed the view that Muslims had "distinct [c]ulture of their own and had the (every) right to persevere it".[16] At this conference, Liaquat Ali Khan announced that:
Soon, Ali Khan and his wife departed to England, but did not terminate his connections with the Muslim League. With Ali Khan departing, the Muslim League's parliamentary wing disintegrated, with many Muslim members joining the either Democratic Party, originally organized by Ali Khan in 1930, and the Congress Party.[16] At the deputation in England, Ali Khan made close study of organizing the political parties, and would soon return to his country with Jinnah.[16]
Round Table conference[edit]
In 1930, Jinnah urged Prime minister Ramsay MacDonald and his Viceroy Lord Irwin to convene a Round Table Conferences in London.[19] In spite of what Jinnah was expecting, the conference was a complete failure, forcing Jinnah to retire from the national politics, and permanently settled in London and was practicing law before the Privy Council.[11][20]
During this time, Ali Khan and his wife joined Jinnah, with Ali Khan practicing the economical law and his wife joined the faculty of economics at the local college. Ali Khan and his wife spent most of their time convincing Jinnah to return to British India to unite the scattered Muslim League mass into one full force.[20][21] Meanwhile, Choudhry Rahmat Ali coined the "Pakstan term in his famous pamphlet Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?.[20] With Rehmat Ali andMohammad Iqbal (who would also take him in confidence of seeing a vision in his dream of a separate Muslim state).[20][21]
Pakistan movement[edit]
When Muhammad Ali Jinnah returned to India, he started to reorganise the Muslim League. In 1936, the annual session of the League met in Bombay (now Mumbai). In the open session on 12 April 1936, Jinnah moved a resolution proposing Khan as the Honorary General Secretary. The resolution was unanimously adopted and he held the office till the establishment of Pakistan in 1947.[22] In 1940, Khan was made the deputy leader of the Muslim League Parliamentary party. Jinnah was not able to take active part in the proceedings of the Assembly on account of his heavy political work. It was Khan who stood in his place. During this period, Khan was also the Honorary General Secretary of the Muslim League, the deputy leader of their party, Convenor of the Action Committee of the Muslim League, Chairman of the Central Parliamentary Board and the managing director of the newspaper Dawn.[23]
The Pakistan Resolution was adopted in 1940 at the Lahore session of the Muslim League. The same year elections were held for the central legislative assembly which were contested by Khan from the Barielly constituency. He was elected without contest. When the twenty-eighth session of the League met in Madras (now Chennai) on 12 April 1941, Jinnah told party members that the ultimate aim was to obtain Pakistan. In this session, Khan moved a resolution incorporating the objectives of the Pakistan Resolution in the aims and objectives of the Muslim League. The resolution was seconded and passed unanimously.[23]
In 1945–46, mass elections were held in India and Khan won the Central Legislature election from the Meerut Constituency in the United Provinces. He was also elected Chairman of the League's Central Parliamentary Board. The Muslim League won 87% of seats reserved for Muslims of British India.[24] He assisted Jinnah in his negotiations with the members of the Cabinet Mission and the leaders of the Congress during the final phases of the Freedom Movement and it was decided that an interim government would be formed consisting of members of the Congress, the Muslim League and minority leaders. When the Government asked the Muslim League to send five nominees for representation in the interim government, Khan was asked to lead the League group in the cabinet. He was given the portfolio of finance.[25] The other four men nominated by the League were Ibrahim Ismail Chundrigar, Ghazanfar Ali Khan, Abdur Rab Nishtar, and Jogendra Nath Mandal.[26] By this point, the British government and the Indian National Congress had both accepted the idea of Pakistan and therefore on 14 August 1947, Pakistan came into existence.[17]
Prime Minister[edit]
After independence, Ali Khan was appointed as the first Prime Minister of Pakistanby the founding fathers of Pakistan. Khan was made the prime minister during the penultimate times, the country was born at the time of starting of the extensive competition between two world superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union.[27] Ali Khan faced with mounted challenges and difficulties while trying to administer the country. Ali Khan and the Muslim League faced with dual competitions with socialists in West-Pakistan and, the communists in East Pakistan.[27] The Muslim League founded difficult to face competition with socialists in West Pakistan, and lost considerable support in favor of socialists led its Marxist leader Faiz Ahmad Faiz. In East Pakistan, the Muslim League's political base was vanished by Pakistan Communist Party after staging a mass protest.[27]
At an internal front, Ali Khan faced with socialist's nationalists challenges and different religious ideologies further pushed the country into more unrest.[27] Problems with Soviet Union and Soviet bloc further escalated after Ali Khan failed to make a visit to Soviet Union, despite his intention.[27] Although, Ali Khan envision the foreign policy more independent, despite his initiatives, the country had become more dependent to the United States which influenced on Ali Khan's policy towards the communist bloc.[27] His government faced eminent challenges and endless regional conflict with India, forcing Ali Khan to approach to his counterpart Jawaharlal Nehru to reach a settlement to end the religious violence, but Nehru pushed for the referral of the problem to the United Nations.[7] Generally an anti-communist, Ali Khan send the recommendation to Jinnah to appointed Abdul Rashid as country's first Chief Justice, and Justice Abdur Rahim as President of Constitutional Assembly, both of them were also the Founding fathers of Pakistan.[27] Earliest reforms Ali Khan took was to centralize the Muslim League, and planned and prepared the Muslim League to become the successor authority of Pakistan.[27]
Economic and education policy[edit]
Main article: Five-Year Plans of Pakistan
Prime minister Liaquat Ali Khan took initiatives to developed educational infrastructure,science and technology in the country, with carrying the vision of successful development of science and technology to aid the essential foreign policy of Pakistan.[28] In 1947, with Jinnah inviting Rafi Muhammad Chaudhry to Pakistan, on the other hand, Liaquat Ali Khan called Salimuzzaman Siddiqui, awarding him the citizenship, and appointed him as his first government science adviser in 1950.[28]During this same time, Ali Khan also called Raziuddin Siddiqui, asking him to plan and establish the educational research institutes in the country.[28] Ali Khan asked Ziauddin Ahmed to draft the educational policy, which was submitted to his office in November 1947, and a road map to establishing the education in the country was quickly adopted by Ali Khan's government.[28]
Ali Khan's government authorized the establishment of the Sindh University.[28] Under his government, the science infrastructure was slowly built but he continued inviting Muslims scientists and engineers from India to Pakistan, believing it essential for Pakistan's future progress.[28]
In 1947, Ali Khan and his Treasure minister Malick Ghulam proposed the idea of Five-Year Plans, by putting the country's economic system on investment and capitalism grounds.[29] Focusing on an initial Planned economic system under the directives of private sector and consortium industries in 1948; the economic planning began to take place in his office, but soon collapse partly because of unsystematic and inadequate staffing.[29] Ali Khan's economic policies were soon heavily became dependent to United States's aid to the country.[29] In spite of planning an independent economic policies, Ali Khan's economic policies focused on the United States' aid programme, on the other hand, Nehru focused on socialism and went on to be a part of Non Aligned Movement.[29] An important event during his premiership was the establishment ofNational Bank in November 1949, and the installation of a paper currency mill in Karachi.[30] Unlike his Indian counterpartJawaharlal Nehru, Ali Khan drew Pakistan's economy planned, but open free market economy, with no government influence.[29]
Immigration problem[edit]
The newly birthed Pakistan faced a number of immigration and naturalization difficulties in its early days. Whilst both Ali Khan and Jinnah were determined to stop the riots and refugee problems and to set up an effective administrative system for the country,[29] Jinnah's plea to regard religion as a personal matter, not a state matter, was completely ignored by both sides.[29] His government was prepared to control the communal rioting and the mass movements of population, but was unable to stop the violence .[29] The inadequate borders and dividing of armed forces between India and Pakistan further escalated the conflict, bringing both militaries at the point of conflict.[29] West-Pakistan lost a large population of Hindus and Sikhs, despite Jinnah's appeal to keep the minorities in Pakistan.[29] Ali Khan's government found it difficult to help the Urdu-speaking population of United Province to settle in Pakistan.[29] While East Pakistan under her Chief Minister Nurul Amin remained peaceful and untouched by the violence and riots, West Pakistan was jolted and badly shaken with violence, riots, massive rape and ill-treatment of children, which brought the international communities to intervene in the conflict.[29]
The immigration of Urdu-speaking communities further polarized the West Pakistani population, especially in the cities of Karachi, Lahore, and other parts of Sindh Province and Balochistan Province (Balochis refused to provide refuge to Urdu-speaking people by using violent policies leading to a Balochistan conflict).[29] In 1951, close to half of the population of Pakistan's major cities were immigrants.[29] According to the United States Government, the casualties stood at approximately 250,000 dead and 12 million to 24 million refugees displaced in India and Pakistan.[29]
Constitutional annex[edit]
Main article: Annex to the Constitution of Pakistan
During his first days, Ali Khan first adopted the 1935 Act to administer the country, although his lawmakers and legislators continued to work on different bill.[31] Finally in 1949 after Jinnah's death, Prime Minister Ali Khan intensified his vision to establish the Islamic system in the country, presenting the Objectives Resolution— a prelude to future constitutions, in theConstituent Assembly.[31] The house passed it on 12 March 1949, but met with harsh critic even from his Law MinisterJogendra Nath Mandal who argued against it.[32] Severe criticism were also raised by MP Ayaz Amir On the other hand, Liquat Ali Khan described as this bill as "Magna Carta" of Pakistan's constitutional history.[33] Khan called it "the most important occasion in the life of this country, next in importance, only to the achievement of independence". Under his leadership, a team of legislators also drafted the first report of the Basic Principle Committee and work began on the second report.[31]
War with India[edit]
Main articles: Indo-Pakistani War of 1947 and Balochistan conflict
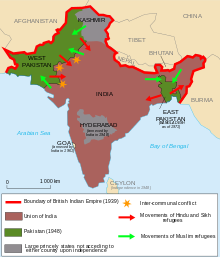
Soon after appointing a new government, Pakistan started a war with India over on Kashmir conflict in 1947–48.[34] The British commander of Pakistan Army General Sir Frank Walter Messervy, KCB,KCIE,CB,CBE,DSO,MC refused to send the army units,General Douglas Gracey was appointed the commander in chief of Pakistan Army, Liaquat Ali Khan ordered the independent units of the Pakistan Army to intervene in the conflict.[35] On Kashmir issue, Ali Khan and Jinnah's policy reflected "Pakistan's alliance with U.S and United Kingdom" against the "Indian imperialism" and "Soviet expansion".[34]However, it is revealed by historians that differences and disagreement with Jinnah arise over on Kashmir issue.[34] Jinnah's strategy to liberate Kashmir was using the military forces.[34] Thus, Jinnah's strategy was to "kill two birds with one stone",[34] namely decapitate India by controlling Kashmir, and to find a domestic solution through foreign and military intervention.[34]
On Ali Khan's personal accounts and views, the prime minister preferred a "harder diplomatic" and "less military stance".[34]The prime minister sought a dialogue with his counterpart, and agreed to resolve the dispute of Kashmir in a peaceful manner through the efforts of the United Nations. According to this agreement a ceasefire was effected in Kashmir on 1 January 1949. It was decided that a free and impartial plebiscite would be held under the supervision of the UN.[36] Prime minister's diplomatic stance was met with hostility by the Pakistan Armed Forces and the socialists and communists, notably the mid-higher level command who would later sponsored an alleged coup led by the communists and socialists against his government.[34]
On southern fronts, Ali Khan's government faced another challenge— the Balochistan conflict.[37] Ali Khan's government send the army units to force tribal leaders to integrate their states with Pakistan.[37] This move met with hostile when Prince Karim Khan, leader of Kalat, initiated a separatist movement against his government.[37] On the night of 16 May 1948, Prince Khan escaped to Afghanistan, conducting a guerrilla warfare based in Afghanistan against the Pakistan Government.[37] This conflict was short-lived when Afghanistan and Soviet Union denied to offer Prince Khan's scheme to dismembered the country



No comments:
Post a Comment